The
oceanic trenches are hemispheric-scale long but narrow topographic depressions of the sea floor. They are also the deepest parts of the ocean floor.
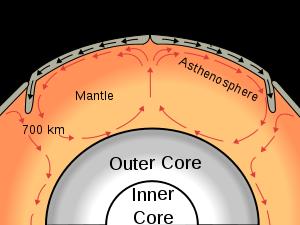
Trenches define one of the most important natural boundaries on the Earth’s solid surface, that between two lithospheric plates. There are three types of lithospheric plate boundaries: divergent (where lithosphere and oceanic crust is created at mid-ocean ridges), convergent (where one lithospheric plate sinks beneath another and returns to the mantle), and transform (where two lithospheric plates slide past each other).
Trenches are a spectacular and distinctive morphological feature of plate boundaries. Plates move together along convergent plate boundaries at convergence rates that vary from a few millimeters to ten or more centimeters per year. A trench marks the position at which the flexed, subducting slab begins to descend beneath another lithospheric slab. Trenches are generally parallel to a volcanic island arc, and about 200 km from a volcanic arc. Oceanic trenches typically extend 3 to 4 km (1.9 to 2.5 mi) below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor. The deepest ocean depth to be sounded is in the Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench at a depth of 10,911 m (35,798 ft) below sea level. Oceanic lithosphere disappears into trenches at a global rate of about a tenth of a square meter per second.